Bohrs model of the molecule 1 Atoms have a nucleus in the middle. Electrons revolve around the nucleus of an atom in fixed paths called orbits or.
Bohr S Atomic Model Overview Importance Expii
3 Certain exceptional circles known as discrete circles of electrons are permitted inside the molecule.

. 4 While rotating in discrete circles the electrons dont transmit energy. 3The electrons revolve around the nucleus in. The energy levels are represented by an integer.
According to this model In an atom the electrons revolve around the nucleus in definite energy levels called orbitsshells. Main ideas of the Bohr model. Bohrs model of the hydrogen atom.
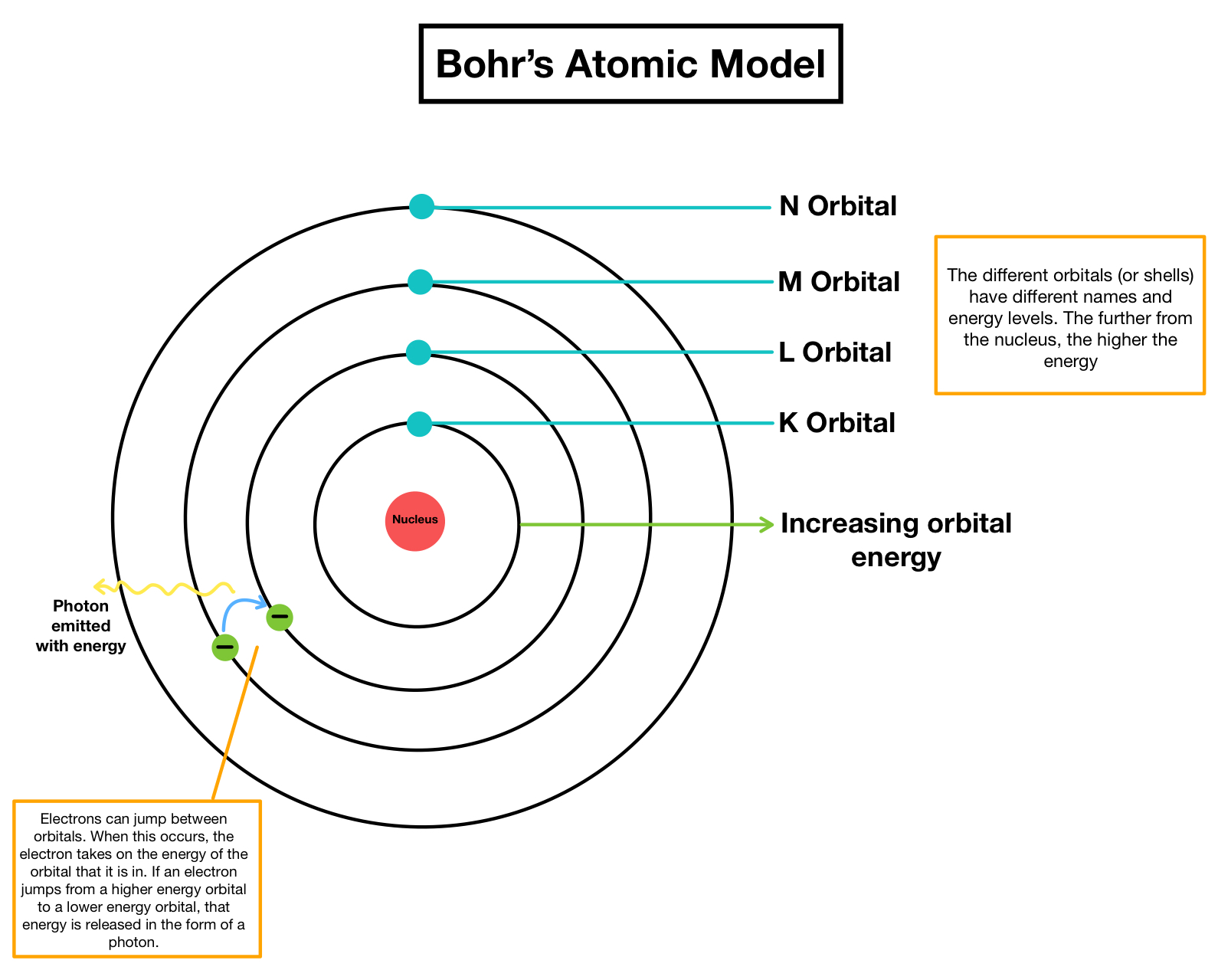
The three levels produce three spectral lines. The change in the energy of an electron occurs when it jumps from lower to higher energy levels. Bohr proposed that electrons do not radiate energy as they orbit the nucleus but exist in states of constant energy which he called stationary states.
Structural model in which an electron moves around the nucleus only in circular orbits each with a specific allowed radius. The postulates given by Neils Bohr are. 2 An atoms energy does not change while the electron moves in a particular orbit.
The Bohr model and all of its successors describe the properties of atomic electrons in terms of a set of allowed possible values. Bohrs model consists of a small nucleus positively charged surrounded by negative electrons moving around the nucleus in orbits where he found out that an electron located away from the nucleus has more energy as compared to electrons close to the nucleus. Electrons revolve around the nucleus in a fixed circular path termed orbits or shells or energy level.
Each orbit or shell has a fixed energy and these circular orbits are known as orbital shells. 2 The nucleus of the atom attracts the electron of the atom but the centrifugal force generated by the circular motion balances this force. Atoms absorb or emit radiation only when the.
A model proposed by Niels Bohr to support his hypothesis about electronsin a hydrogen atom. An atom consists of electrons and protons in an atom protons are in its nucleus and electrons are outside the nucleus. In atomic physics the Bohr model if the atom also known as the Rutherford-Bohr model is modern model of the hydrogen atom introduced by Danish physicist Niels Bohr working with Ernest Rutherford at the University of Manchester in 1913.
2 Electrons rotate around the nucleus. The model proposes that the maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in any particular orbit is 2n 2 where n is the number of orbits. Neil Bohr put forward the following postulates about the model of an atom.
Bohrs model of an atom 1An atom is made up of three particleselectronsprotons and neutronsElectrons have negative chargeprotons have. 2The protons and neutrons are located in a small nucleus at the centre of an atomDue to the presence of. I Atoms has nucleus that is present in the centre.
When it gains energy it excites from lower to higher and vice versa. According to Bohr model the revolving paths traced by electrons are called orbits or shells. 5 These circles or shells are called energy levels.
The model was proposed by physicist Niels Bohr in 1913. Postulates of Bohrs Model of an Atom In an atom electrons negatively charged revolve around the positively charged nucleus in a definite circular path. Bohrs Model of an atom.
Bohrs model of the atom accounted for the general chemical properties of the elements even leading to the discovery of a new elementhafnium. This is a model of the atomic structure in which electronstravel around the nucleus in well-defined orbits determined by quantumconditions. Bohrs Model is an atomic model proposed by a Danish Physicist Niels Bohr in 1913.
1 In an atom the electrons rotate in circular orbits around the nucleus. Every circular orbit will have a certain amount of fixed energy and these circular orbits were termed. This model provides especially the solution to the problem of the failure of classical physics in the field.
The orbiting electron does not normally emit electromagnetic radiation but does so when changing from one orbit to another. Bohr solved the. 2 days agoAnd that Bohrs New Model enthusiasts is your lot for today.
As electrons move from higher-energy to lower-energy levels energy in. The Bohr model of the atom established the existence of a positive nucleus surrounded by electrons in specific energy levels. The orbits are termed as stationary orbit.
The Bohr Model of The Atom 1 The H atom only has certain energy levels they are determined by fixed circular orbits of electrons around the nucleus. While largely obsolete today in practical terms Bohrs model for the atom is. Describe Bohrs model of the atom.
1 day agoTo assist describe this Bohr recommended that the feasible orbit s in a hydrogen atom rise by n 2 where n is the primary quantum number According to Bohrs design a covering 3 to shell 2 shift creates the initial line of the Balmer collection For hydrogen this makes a photon having a wavelength of 656 nm or traffic signal as seen. In this model the electrons travel around the nucleus of an atom in distinct circular orbits or shells. Following the discoveries of hydrogen emission spectra and the photoelectric effect the Danish physicist Niels Bohr 18851962 proposed a new model of the atom in 1915.
Thus energy is not lost and the atom remains stable. Bohr model is utilized for giving a lucid explanation to the features of an atom. The model is also referred to as the planetary model of an atom.
Ii There are only certain special orbits known as discrete orbits in which the electrons revolve around the nucleus are known to be present inside the atom. The Bohr model of the atom a radical departure from earlier classical descriptions was the first that incorporated quantum theory and was the predecessor of wholly quantum-mechanical models. The Bohr Model is a structural model of an atom.
Bohrs explanation of the Rydberg-Ritz combination principle is shown in Figure 5 which shows three of many levels in an atom. Electrons revolve around the nucleus of an atom in fixed paths called orbits or shells. Bohr explained the stability through the concept of the revolution of electrons in different energy levels.
A transition from a higher orbit to a lower orbit will releasequantized energies of light which would explain the light spectrum.

Bohr S Atomic Model Overview Importance Expii

The Bohr Model Introduction To Chemistry

Bohr S Model Of An Atom With Postulates And Limitations Of Bohr S Model Bohr Model Applicable To

1 Comments
This information is very helpful, Thank You for sharing such valuable information with us.Nursery schools in bangalore
ReplyDelete